- Home
- About us
- ENT Services
- EAR Surgeries
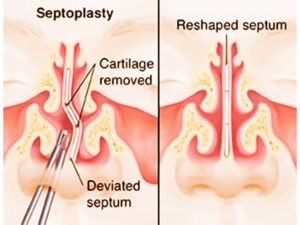
- NOSE Surgeries
- THROAT Surgeries
- Laryngeal Surgeries
- Head & Neck Surgeries
- Thyroid Surgery
- Parathyroid Surgery
- Salivary Gland Surgery
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Neck Dissection
- Reconstructive Surgery
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS)
- Laryngectomy
- Oropharyngeal
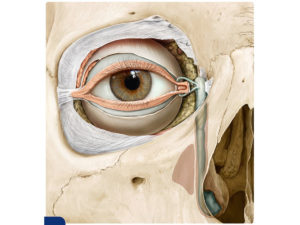
- Facial Trauma Surgery
- Skull Base Surgery
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Surgery
- Branchial Cleft Cyst Surgery
- Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy
- Parotidectomy
- Paediatric ENT
- Psychiatry Services
- Gallery
- Contact Us